- Estonia
-
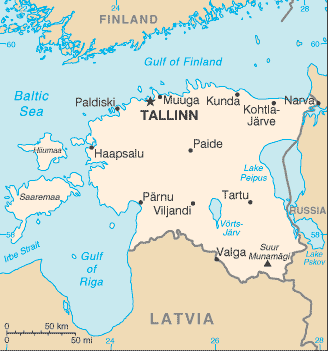 Introduction ::EstoniaBackground:After centuries of Danish, Swedish, German, and Russian rule, Estonia attained independence in 1918. Forcibly incorporated into the USSR in 1940 - an action never recognized by the US - it regained its freedom in 1991 with the collapse of the Soviet Union. Since the last Russian troops left in 1994, Estonia has been free to promote economic and political ties with the West. It joined both NATO and the EU in the spring of 2004, formally joined the OECD in late 2010, and adopted the euro as its official currency on 1 January 2011.Geography ::EstoniaLocation:Eastern Europe, bordering the Baltic Sea and Gulf of Finland, between Latvia and RussiaGeographic coordinates:59 00 N, 26 00 EArea:total: 45,228 sq kmcountry comparison to the world: 133land: 42,388 sq kmwater: 2,840 sq kmnote: includes 1,520 islands in the Baltic SeaArea - comparative:slightly smaller than New Hampshire and Vermont combinedLand boundaries:total: 633 kmborder countries: Latvia 343 km, Russia 290 kmCoastline:3,794 kmMaritime claims:territorial sea: 12 nmexclusive economic zone: limits fixed in coordination with neighboring statesClimate:maritime; wet, moderate winters, cool summersTerrain:marshy, lowlands; flat in the north, hilly in the southElevation extremes:lowest point: Baltic Sea 0 mhighest point: Suur Munamagi 318 mNatural resources:oil shale, peat, rare earth elements, phosphorite, clay, limestone, sand, dolomite, arable land, sea mudLand use:arable land: 13.97%permanent crops: 0.13%other: 85.89% (2011)Irrigated land:4.58 sq km (2010)Total renewable water resources:12.81 cu km (2011)Freshwater withdrawal (domestic/industrial/agricultural):total: 1.8 cu km/yr (3%/97%/0%)per capita: 1,337 cu m/yr (2009)Natural hazards:sometimes flooding occurs in the springEnvironment - current issues:air polluted with sulfur dioxide from oil-shale burning power plants in northeast; however, the amount of pollutants emitted to the air have fallen steadily, the emissions of 2000 were 80% less than in 1980; the amount of unpurified wastewater discharged to water bodies in 2000 was 1/20 the level of 1980; in connection with the start-up of new water purification plants, the pollution load of wastewater decreased; Estonia has more than 1,400 natural and manmade lakes, the smaller of which in agricultural areas need to be monitored; coastal seawater is polluted in certain locationsEnvironment - international agreements:party to: Air Pollution, Air Pollution-Nitrogen Oxides, Air Pollution-Persistent Organic Pollutants, Air Pollution-Sulfur 85, Air Pollution-Volatile Organic Compounds, Antarctic Treaty, Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Wetlandssigned, but not ratified: none of the selected agreementsGeography - note:the mainland terrain is flat, boggy, and partly wooded; offshore lie more than 1,500 islandsPeople and Society ::EstoniaNationality:noun: Estonian(s)adjective: EstonianEthnic groups:Estonian 68.7%, Russian 25.6%, Ukrainian 2.1%, Belarusian 1.2%, Finn 0.8%, other 1.6% (2008 census)Languages:Estonian (official) 67.3%, Russian 29.7%, other 2.3%, unknown 0.7% (2000 census)Religions:Evangelical Lutheran 13.6%, Orthodox 12.8%, other Christian (including Methodist, Seventh-Day Adventist, Roman Catholic, Pentecostal) 1.4%, unaffiliated 34.1%, other and unspecified 32%, none 6.1% (2000 census)Population:1,266,375 (July 2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 157Age structure:0-14 years: 15.4% (male 100,605/female 94,831)15-24 years: 11.9% (male 77,302/female 73,446)25-54 years: 41.3% (male 250,997/female 272,460)55-64 years: 13.1% (male 71,442/female 94,278)65 years and over: 18.2% (male 76,356/female 154,658) (2013 est.)Dependency ratios:total dependency ratio: 51.2 %youth dependency ratio: 23.9 %elderly dependency ratio: 27.3 %potential support ratio: 3.7 (2013)Median age:total: 41 yearsmale: 37.4 yearsfemale: 44.3 years (2013 est.)Population growth rate:-0.66% (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 229Birth rate:10.38 births/1,000 population (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 185Death rate:13.65 deaths/1,000 population (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 14Net migration rate:-3.35 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 183Urbanization:urban population: 69.5% of total population (2011)rate of urbanization: 0.02% annual rate of change (2010-15 est.)Major urban areas - population:TALLINN (capital) 399,000 (2009)Sex ratio:at birth: 1.06 male(s)/female0-14 years: 1.06 male(s)/female15-24 years: 1.05 male(s)/female25-54 years: 0.92 male(s)/female55-64 years: 0.76 male(s)/female65 years and over: 0.49 male(s)/femaletotal population: 0.84 male(s)/female (2013 est.)Mother's mean age at first birth:26.3 (2010 est.)Maternal mortality rate:2 deaths/100,000 live births (2010)country comparison to the world: 184Infant mortality rate:total: 6.82 deaths/1,000 live birthscountry comparison to the world: 164male: 7.94 deaths/1,000 live birthsfemale: 5.63 deaths/1,000 live births (2013 est.)Life expectancy at birth:total population: 73.82 yearscountry comparison to the world: 118male: 68.58 yearsfemale: 79.4 years (2013 est.)Total fertility rate:1.45 children born/woman (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 198Contraceptive prevalence rate:63.4%note: percent of women aged 18-49 (2005)Health expenditures:6% of GDP (2010)country comparison to the world: 107Physicians density:3.41 physicians/1,000 population (2008)Hospital bed density:5.4 beds/1,000 population (2009)Drinking water source:improved:urban: 99% of populationrural: 97% of populationtotal: 98% of populationunimproved:urban: 1% of populationrural: 3% of populationtotal: 2% of population (2010 est.)Sanitation facility access:improved:urban: 96% of populationrural: 94% of populationtotal: 95% of populationunimproved:urban: 4% of populationrural: 6% of populationtotal: 5% of population (2010 est.)HIV/AIDS - adult prevalence rate:1.2% (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 43HIV/AIDS - people living with HIV/AIDS:9,900 (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 97HIV/AIDS - deaths:fewer than 500 (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 97Major infectious diseases:degree of risk: intermediatevectorborne disease: tickborne encephalitis (2013)Obesity - adult prevalence rate:20.6% (2008)country comparison to the world: 95Education expenditures:6.1% of GDP (2009)country comparison to the world: 37Literacy:definition: age 15 and over can read and writetotal population: 99.8%male: 99.8%female: 99.8% (2011 est.)School life expectancy (primary to tertiary education):total: 16 yearsmale: 15 yearsfemale: 17 years (2010)Unemployment, youth ages 15-24:total: 22.4%country comparison to the world: 46male: 23.8%female: 20.7% (2011)Government ::EstoniaCountry name:conventional long form: Republic of Estoniaconventional short form: Estonialocal long form: Eesti Vabariiklocal short form: Eestiformer: Estonian Soviet Socialist RepublicGovernment type:parliamentary republicCapital:name: Tallinngeographic coordinates: 59 26 N, 24 43 Etime difference: UTC+2 (7 hours ahead of Washington, DC during Standard Time)daylight saving time: +1hr, begins last Sunday in March; ends last Sunday in OctoberAdministrative divisions:15 counties (maakonnad, singular - maakond); Harjumaa (Tallinn), Hiiumaa (Kardla), Ida-Virumaa (Johvi), Jarvamaa (Paide), Jogevamaa (Jogeva), Laanemaa (Haapsalu), Laane-Virumaa (Rakvere), Parnumaa (Parnu), Polvamaa (Polva), Raplamaa (Rapla), Saaremaa (Kuressaare), Tartumaa (Tartu), Valgamaa (Valga), Viljandimaa (Viljandi), Vorumaa (Voru)note: counties have the administrative center name following in parenthesesIndependence:20 August 1991 (declared); 6 September 1991 (recognized by the Soviet Union)National holiday:Independence Day, 24 February (1918); note - 24 February 1918 was the date Estonia declared its independence from Soviet Russia and established its statehood; 20 August 1991 was the date it declared its independence from the Soviet UnionConstitution:adopted 28 June 1992Legal system:civil law systemInternational law organization participation:accepts compulsory ICJ jurisdiction with reservations; accepts ICCt jurisdictionSuffrage:18 years of age; universal for all Estonian citizensExecutive branch:chief of state: President Toomas Hendrik ILVES (since 9 October 2006)head of government: Prime Minister Andrus ANSIP (since 12 April 2005)cabinet: Ministers appointed by the prime minister, approved by Parliament(For more information visit the World Leaders website )elections: president elected by Parliament for a five-year term (eligible for a second term); if a candidate does not secure two-thirds of the votes after three rounds of balloting in the Parliament, then an electoral assembly (made up of Parliament plus members of local councils) elects the president, choosing between the two candidates with the largest number of votes; election last held on 29 August 2011 (next to be held in the fall of 2016); prime minister nominated by the president and approved by Parliamentelection results: Toomas Hendrik ILVES reelected president; parliamentary vote - Toomas Hendrik ILVES 73, Indrek TARAND 25Legislative branch:unicameral Parliament or Riigikogu (101 seats; members elected by popular vote to serve four-year terms)elections: last held on 6 March 2011 (next to be held in March 2015)election results: percent of vote by party - Estonian Reform Party 28.6%, Center Party of Estonia 23.3%, IRL 20.5%, SDE 17.1%, Estonian Greens 3.8%, Estonian People's Union 2.1%, other 4.6%; seats by party - Estonian Reform Party 33, Center Party 21, IRL 23, SDE 19, unaffiliated 5Judicial branch:highest court(s): Supreme Court (consists of the chief justice and organized into the Civil Chamber with a chamber chairman and 6 justices, the Criminal Chamber with a chamber chairman and 5 justices, the Administrative Law Chamber with a chamber chairman and 4 justices, and the Constitutional Review Chamber with 9 members - the chief justice and 2 justices from the Civil Chamber, 3 from the Criminal Chamber and 3 from the Administrative chamber)judge selection and term of office: the chief justice is proposed by the president and appointed by the Riigikogu; other justices proposed by the chief justice and appointed by the Riigikogu; justices appointed for lifesubordinate courts: circuit (appellate) courts; administrative, county, city, and specialized courtsPolitical parties and leaders:Center Party of Estonia (Keskerakond) [Edgar SAVISAAR]Estonian Greens (Rohelised) [Aleksander LAANE]Estonian Conservative People's Party (Konservatiivne Rahvaerakond) or EKRE [Margo MILJAND]Estonian Reform Party (Reformierakond) [Andrus ANSIP]Social Democratic Party or SDE [Sven MIKSER]Union of Pro Patria and Res Publica (Isamaa je Res Publica Liit) or IRL [Urmas REINSALU]International organization participation:Australia Group, BA, BIS, CBSS, CD, CE, EAPC, EBRD, ECB, EIB, EMU, ESA (cooperating state), EU, FAO, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC (national committees), ICRM, IDA, IFC, IFRCS, IHO, ILO, IMF, IMO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, ITUC (NGOs), MIGA, NATO, NIB, NSG, OAS (observer), OECD, OIF (observer), OPCW, OSCE, PCA, Schengen Convention, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNHCR, UNTSO, UPU, WCO, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTODiplomatic representation in the US:chief of mission: Ambassador Marina KALJURANDchancery: 2131 Massachusetts Avenue NW, Washington, DC 20008telephone: [1] (202) 588-0101FAX: [1] (202) 588-0108consulate(s) general: New YorkDiplomatic representation from the US:chief of mission: Ambassador Jeffrey LEVINEembassy: Kentmanni 20, 15099 Tallinnmailing address: use embassy street addresstelephone: [372] 668-8100FAX: [372] 668-8134Flag description:three equal horizontal bands of blue (top), black, and white; various interpretations are linked to the flag colors; blue represents faith, loyalty, and devotion, while also reminiscent of the sky, sea, and lakes of the country; black symbolizes the soil of the country and the dark past and suffering endured by the Estonian people; white refers to the striving towards enlightenment and virtue, and is the color of birch bark and snow, as well as summer nights illuminated by the midnight sunNational symbol(s):barn swallow, cornflowerNational anthem:name: ""Mu isamaa, mu onn ja room"" (My Native Land, My Pride and Joy)lyrics/music: Johann Voldemar JANNSEN/Fredrik PACIUSnote: adopted 1920, though banned between 1940 and 1990 under Soviet occupation; the anthem, used in Estonia since 1869, shares the same melody with that of Finland but has different lyricsEconomy ::EstoniaEconomy - overview:Estonia, a member of the European Union and the eurozone since 2004, has a modern market-based economy and one of the higher per capita income levels in Central Europe and the Baltic region. Estonia's successive governments have pursued a free market, pro-business economic agenda and have wavered little in their commitment to pro-market reforms. The current government has followed sound fiscal policies that have resulted in balanced budgets and low public debt. The economy benefits from strong electronics and telecommunications sectors and strong trade ties with Finland, Sweden, Russia, and Germany. Tallinn's priority has been to sustain high growth rates - on average 8% per year from 2003 to 2007. Estonia's economy fell into recession in mid-2008 with GDP contracting 14.3% in 2009, as a result of an investment and consumption slump following the bursting of the real estate market bubble and a decrease in export demand as result of economic slowdown in the rest of Europe. Estonia rebounded nearly 8% in 2011 and the Estonian economy now has one of the higher GDP growth rates in Europe. Estonia adopted the euro on 1 January 2011.GDP (purchasing power parity):$29.57 billion (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 113$28.64 billion (2011 est.)$26.45 billion (2010 est.)note: data are in 2012 US dollarsGDP (official exchange rate):$21.86 billion (2012 est.)GDP - real growth rate:3.2% (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 1038.3% (2011 est.)3.3% (2010 est.)GDP - per capita (PPP):$22,100 (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 66$21,400 (2011 est.)$19,700 (2010 est.)note: data are in 2012 US dollarsGross national saving:24.1% of GDP (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 5026.9% of GDP (2011 est.)23.1% of GDP (2010 est.)GDP - composition, by end use:household consumption: 50.1%government consumption: 18.8%investment in fixed capital: 24.5%investment in inventories: 5.8%exports of goods and services: 89.1%imports of goods and services: -88.3%(2012 est.)GDP - composition, by sector of origin:agriculture: 3.9%industry: 29.7%services: 66.4% (2012 est.)Agriculture - products:grain, potatoes, vegetables; livestock and dairy products; fishIndustries:engineering, electronics, wood and wood products, textiles; information technology, telecommunicationsIndustrial production growth rate:2.2% (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 95Labor force:695,000 (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 152Labor force - by occupation:agriculture: 4.2%industry: 20.2%services: 75.6% (2010)Unemployment rate:10.2% (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 10912.5% (2011 est.)Population below poverty line:17.5% (2010)Household income or consumption by percentage share:lowest 10%: 2.7%highest 10%: 27.7% (2004)Distribution of family income - Gini index:31.3 (2010)country comparison to the world: 10837 (1999)Budget:revenues: $8.144 billionexpenditures: $8.201 billion (2012 est.)Taxes and other revenues:37.2% of GDP (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 56Budget surplus (+) or deficit (-):-0.3% of GDP (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 53Public debt:5.7% of GDP (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 1505.9% of GDP (2011 est.)note: data cover general government debt, and includes debt instruments issued (or owned) by government entities, including sub-sectors of central government, state government, local government, and social security fundsFiscal year:calendar yearInflation rate (consumer prices):3.9% (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 1215% (2011 est.)Commercial bank prime lending rate:8% (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 1396.12% (31 December 2011 est.)Stock of narrow money:$8.104 billion (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 82$6.744 billion (31 December 2011 est.)note: this figure represents the US dollar value of Estonian kroon in circulation prior to Estonia's joining the Economic and Monetary Union (EMU); see entry for the European Union for money supply in the euro area; the European Central Bank (ECB) controls monetary policy for the 17 members of the EMU; individual members of the EMU do not control the quantity of money circulating within their own bordersStock of broad money:$12.11 billion (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 99$11.73 billion (31 December 2011 est.)Stock of domestic credit:$19.04 billion (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 85$19.14 billion (31 December 2011 est.)Market value of publicly traded shares:$1.611 billion (31 December 2011)country comparison to the world: 97$2.26 billion (31 December 2010)$2.654 billion (31 December 2009)Current account balance:$498 million (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 47$477 million (2011 est.)Exports:$16.16 billion (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 78$16.78 billion (2011 est.)Exports - commodities:machinery and electrical equipment 21%, wood and wood products 9%, metals 9%, furniture 7%, vehicles and parts 5%, food products and beverages 4%, textiles 4%, plastics 3%Exports - partners:Sweden 16.8%, Finland 15.3%, Russia 12.7%, Latvia 9.2%, Lithuania 5.7%, Germany 4.8% (2012)Imports:$17.05 billion (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 83$17.09 billion (2011 est.)Imports - commodities:machinery and electrical equipment, mineral fuels, chemical products, foodstuffs, plastics, textilesImports - partners:Finland 15.1%, Germany 10.7%, Sweden 10.7%, Latvia 10%, Lithuania 9%, Poland 6.6%, China 4.4%, Russia 4.1% (2012)Reserves of foreign exchange and gold:$246.4 million (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 156$207.5 million (31 December 2011 est.)Debt - external:$25.55 billion (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 77$25.01 billion (31 December 2011 est.)Stock of direct foreign investment - at home:$17.45 billion (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 70$16.65 billion (31 December 2011 est.)Stock of direct foreign investment - abroad:$6.609 billion (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 61$7.359 billion (31 December 2011 est.)Exchange rates:kroon (EEK) per US dollar -0.778 (2012 est.)0.72 (2011 est.)11.81 (2010 est.)11.23 (2009)10.7 (2008)Energy ::EstoniaElectricity - production:12.89 billion kWh (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 88Electricity - consumption:7.755 billion kWh (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 95Electricity - exports:4.354 billion kWh (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 30Electricity - imports:1.1 billion kWh (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 62Electricity - installed generating capacity:2.661 million kW (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 91Electricity - from fossil fuels:94.6% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 69Electricity - from nuclear fuels:0% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 83Electricity - from hydroelectric plants:0.3% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 145Electricity - from other renewable sources:5.1% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 36Crude oil - production:7,700 bbl/day (2011 est.)country comparison to the world: 83Crude oil - exports:0 bbl/day (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 105Crude oil - imports:0 bbl/day (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 179Crude oil - proved reserves:0 bbl (1 January 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 127Refined petroleum products - production:0 bbl/day (2008 est.)country comparison to the world: 173Refined petroleum products - consumption:26,340 bbl/day (2011 est.)country comparison to the world: 121Refined petroleum products - exports:0 bbl/day (2008 est.)country comparison to the world: 173Refined petroleum products - imports:23,270 bbl/day (2008 est.)country comparison to the world: 100Natural gas - production:0 cu m (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 123Natural gas - consumption:701 million cu m (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 96Natural gas - exports:0 cu m (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 92Natural gas - imports:701 million cu m (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 64Natural gas - proved reserves:0 cu m (1 January 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 131Carbon dioxide emissions from consumption of energy:20.56 million Mt (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 81Communications ::EstoniaTelephones - main lines in use:471,900 (2011)country comparison to the world: 101Telephones - mobile cellular:1.863 million (2011)country comparison to the world: 142Telephone system:general assessment: foreign investment in the form of joint business ventures greatly improved telephone service with a wide range of high quality voice, data, and Internet services availabledomestic: substantial fiber-optic cable systems carry telephone, TV, and radio traffic in the digital mode; Internet services are widely available; schools and libraries are connected to the Internet, a large percentage of the population files income-tax returns online, and online voting was used for the first time in the 2005 local electionsinternational: country code - 372; fiber-optic cables to Finland, Sweden, Latvia, and Russia provide worldwide packet-switched service; 2 international switches are located in Tallinn (2011)Broadcast media:the publicly owned broadcaster, Eesti Rahvusringhaaling (ERR), operates 2 TV channels and 5 radio networks; growing number of private commercial radio stations broadcasting nationally, regionally, and locally; fully transitioned to digital television in 2010; national private TV channels expanding service; a range of channels are aimed at Russian-speaking viewers; high penetration rate for cable TV services with more than half of Estonian households connected (2008)Internet country code:.eeInternet hosts:865,494 (2012)country comparison to the world: 49Internet users:971,700 (2009)country comparison to the world: 102Transportation ::EstoniaAirports:18 (2013)country comparison to the world: 141Airports - with paved runways:total: 13over 3,047 m: 22,438 to 3,047 m: 81,524 to 2,437 m: 2914 to 1,523 m: 1 (2013)Airports - with unpaved runways:total: 51,524 to 2,437 m: 1914 to 1,523 m: 1under 914 m:3 (2013)Heliports:1 (2012)Pipelines:gas 868 km (2013)Railways:total: 1,196 kmcountry comparison to the world: 85broad gauge: 1,196 km 1.520-m and 1.524-m gauge (133 km electrified) (2011)Roadways:total: 58,412 km (includes urban roads)country comparison to the world: 75paved: 10,427 km (includes 115 km of expressways)unpaved: 47,985 km (2011)Waterways:335 km (320 km are navigable year round) (2011)country comparison to the world: 91Merchant marine:total: 25country comparison to the world: 89by type: cargo 4, chemical tanker 1, passenger/cargo 18, petroleum tanker 2foreign-owned: 3 (Germany 1, Norway 2)registered in other countries: 63 (Antigua and Barbuda 10, Belize 1, Cambodia 1, Canada 1, Cook Islands 1, Cyprus 6, Dominica 6, Finland 2, Latvia 3, Malta 16, Russia 1, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines 8, Sierra Leone 2, Sweden 3, Venezuela 1, unknown 1) (2010)Ports and terminals:major seaport(s): Kuivastu, Kunda, Muuga, Parnu Reid, Sillamae, TallinnMilitary ::EstoniaMilitary branches:Estonian Defense Forces (Eesti Kaitsevagi): Land Force (Maavagi), Navy (Merevagi), Air Force (Ohuvagi), Defense League (Kaitseliit) (2012)Military service age and obligation:18-27 for compulsory military or governmental service, conscript service requirement 8-11 months depending on education; NCOs, reserve officers, and specialists serve 11 months (2013)Manpower available for military service:males age 16-49: 291,801females age 16-49: 302,696 (2010 est.)Manpower fit for military service:males age 16-49: 210,854females age 16-49: 251,185 (2010 est.)Manpower reaching militarily significant age annually:male: 6,668female: 6,309 (2010 est.)Military expenditures:2% of GDP (2005 est.)country comparison to the world: 67Transnational Issues ::EstoniaDisputes - international:Russia and Estonia in May 2005 signed a technical border agreement, but Russia in June 2005 recalled its signature after the Estonian parliament added to its domestic ratification act a historical preamble referencing the Soviet occupation and Estonia's pre-war borders under the 1920 Treaty of Tartu; Russia contends that the preamble allows Estonia to make territorial claims on Russia in the future, while Estonian officials deny that the preamble has any legal impact on the treaty text; Russia demands better treatment of the Russian-speaking population in Estonia; as a member state that forms part of the EU's external border, Estonia implements strict Schengen border rules with RussiaRefugees and internally displaced persons:stateless persons: 94,235 (2012); note - after becoming independent in 1991, automatic citizenship was restricted to those who were Estonian citizens prior to the 1990 Soviet occupation and their descendants; thousands of ethnic Russians remained stateless when forced to choose between passing Estonian language and citizenship tests or applying for Russian citizenship; one reason for demurring on Estonian citizenship was to retain the right of visa-free travel to Russia; stateless residents can vote in local elections but not general elections; stateless parents who have been lawful residents of Estonia for at least five years can apply for citizenship for their children before they turn 15Illicit drugs:growing producer of synthetic drugs; increasingly important transshipment zone for cannabis, cocaine, opiates, and synthetic drugs since joining the European Union and the Schengen Accord; potential money laundering related to organized crime and drug trafficking is a concern, as is possible use of the gambling sector to launder funds; major use of opiates and ecstasy"
Introduction ::EstoniaBackground:After centuries of Danish, Swedish, German, and Russian rule, Estonia attained independence in 1918. Forcibly incorporated into the USSR in 1940 - an action never recognized by the US - it regained its freedom in 1991 with the collapse of the Soviet Union. Since the last Russian troops left in 1994, Estonia has been free to promote economic and political ties with the West. It joined both NATO and the EU in the spring of 2004, formally joined the OECD in late 2010, and adopted the euro as its official currency on 1 January 2011.Geography ::EstoniaLocation:Eastern Europe, bordering the Baltic Sea and Gulf of Finland, between Latvia and RussiaGeographic coordinates:59 00 N, 26 00 EArea:total: 45,228 sq kmcountry comparison to the world: 133land: 42,388 sq kmwater: 2,840 sq kmnote: includes 1,520 islands in the Baltic SeaArea - comparative:slightly smaller than New Hampshire and Vermont combinedLand boundaries:total: 633 kmborder countries: Latvia 343 km, Russia 290 kmCoastline:3,794 kmMaritime claims:territorial sea: 12 nmexclusive economic zone: limits fixed in coordination with neighboring statesClimate:maritime; wet, moderate winters, cool summersTerrain:marshy, lowlands; flat in the north, hilly in the southElevation extremes:lowest point: Baltic Sea 0 mhighest point: Suur Munamagi 318 mNatural resources:oil shale, peat, rare earth elements, phosphorite, clay, limestone, sand, dolomite, arable land, sea mudLand use:arable land: 13.97%permanent crops: 0.13%other: 85.89% (2011)Irrigated land:4.58 sq km (2010)Total renewable water resources:12.81 cu km (2011)Freshwater withdrawal (domestic/industrial/agricultural):total: 1.8 cu km/yr (3%/97%/0%)per capita: 1,337 cu m/yr (2009)Natural hazards:sometimes flooding occurs in the springEnvironment - current issues:air polluted with sulfur dioxide from oil-shale burning power plants in northeast; however, the amount of pollutants emitted to the air have fallen steadily, the emissions of 2000 were 80% less than in 1980; the amount of unpurified wastewater discharged to water bodies in 2000 was 1/20 the level of 1980; in connection with the start-up of new water purification plants, the pollution load of wastewater decreased; Estonia has more than 1,400 natural and manmade lakes, the smaller of which in agricultural areas need to be monitored; coastal seawater is polluted in certain locationsEnvironment - international agreements:party to: Air Pollution, Air Pollution-Nitrogen Oxides, Air Pollution-Persistent Organic Pollutants, Air Pollution-Sulfur 85, Air Pollution-Volatile Organic Compounds, Antarctic Treaty, Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Wetlandssigned, but not ratified: none of the selected agreementsGeography - note:the mainland terrain is flat, boggy, and partly wooded; offshore lie more than 1,500 islandsPeople and Society ::EstoniaNationality:noun: Estonian(s)adjective: EstonianEthnic groups:Estonian 68.7%, Russian 25.6%, Ukrainian 2.1%, Belarusian 1.2%, Finn 0.8%, other 1.6% (2008 census)Languages:Estonian (official) 67.3%, Russian 29.7%, other 2.3%, unknown 0.7% (2000 census)Religions:Evangelical Lutheran 13.6%, Orthodox 12.8%, other Christian (including Methodist, Seventh-Day Adventist, Roman Catholic, Pentecostal) 1.4%, unaffiliated 34.1%, other and unspecified 32%, none 6.1% (2000 census)Population:1,266,375 (July 2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 157Age structure:0-14 years: 15.4% (male 100,605/female 94,831)15-24 years: 11.9% (male 77,302/female 73,446)25-54 years: 41.3% (male 250,997/female 272,460)55-64 years: 13.1% (male 71,442/female 94,278)65 years and over: 18.2% (male 76,356/female 154,658) (2013 est.)Dependency ratios:total dependency ratio: 51.2 %youth dependency ratio: 23.9 %elderly dependency ratio: 27.3 %potential support ratio: 3.7 (2013)Median age:total: 41 yearsmale: 37.4 yearsfemale: 44.3 years (2013 est.)Population growth rate:-0.66% (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 229Birth rate:10.38 births/1,000 population (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 185Death rate:13.65 deaths/1,000 population (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 14Net migration rate:-3.35 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 183Urbanization:urban population: 69.5% of total population (2011)rate of urbanization: 0.02% annual rate of change (2010-15 est.)Major urban areas - population:TALLINN (capital) 399,000 (2009)Sex ratio:at birth: 1.06 male(s)/female0-14 years: 1.06 male(s)/female15-24 years: 1.05 male(s)/female25-54 years: 0.92 male(s)/female55-64 years: 0.76 male(s)/female65 years and over: 0.49 male(s)/femaletotal population: 0.84 male(s)/female (2013 est.)Mother's mean age at first birth:26.3 (2010 est.)Maternal mortality rate:2 deaths/100,000 live births (2010)country comparison to the world: 184Infant mortality rate:total: 6.82 deaths/1,000 live birthscountry comparison to the world: 164male: 7.94 deaths/1,000 live birthsfemale: 5.63 deaths/1,000 live births (2013 est.)Life expectancy at birth:total population: 73.82 yearscountry comparison to the world: 118male: 68.58 yearsfemale: 79.4 years (2013 est.)Total fertility rate:1.45 children born/woman (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 198Contraceptive prevalence rate:63.4%note: percent of women aged 18-49 (2005)Health expenditures:6% of GDP (2010)country comparison to the world: 107Physicians density:3.41 physicians/1,000 population (2008)Hospital bed density:5.4 beds/1,000 population (2009)Drinking water source:improved:urban: 99% of populationrural: 97% of populationtotal: 98% of populationunimproved:urban: 1% of populationrural: 3% of populationtotal: 2% of population (2010 est.)Sanitation facility access:improved:urban: 96% of populationrural: 94% of populationtotal: 95% of populationunimproved:urban: 4% of populationrural: 6% of populationtotal: 5% of population (2010 est.)HIV/AIDS - adult prevalence rate:1.2% (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 43HIV/AIDS - people living with HIV/AIDS:9,900 (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 97HIV/AIDS - deaths:fewer than 500 (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 97Major infectious diseases:degree of risk: intermediatevectorborne disease: tickborne encephalitis (2013)Obesity - adult prevalence rate:20.6% (2008)country comparison to the world: 95Education expenditures:6.1% of GDP (2009)country comparison to the world: 37Literacy:definition: age 15 and over can read and writetotal population: 99.8%male: 99.8%female: 99.8% (2011 est.)School life expectancy (primary to tertiary education):total: 16 yearsmale: 15 yearsfemale: 17 years (2010)Unemployment, youth ages 15-24:total: 22.4%country comparison to the world: 46male: 23.8%female: 20.7% (2011)Government ::EstoniaCountry name:conventional long form: Republic of Estoniaconventional short form: Estonialocal long form: Eesti Vabariiklocal short form: Eestiformer: Estonian Soviet Socialist RepublicGovernment type:parliamentary republicCapital:name: Tallinngeographic coordinates: 59 26 N, 24 43 Etime difference: UTC+2 (7 hours ahead of Washington, DC during Standard Time)daylight saving time: +1hr, begins last Sunday in March; ends last Sunday in OctoberAdministrative divisions:15 counties (maakonnad, singular - maakond); Harjumaa (Tallinn), Hiiumaa (Kardla), Ida-Virumaa (Johvi), Jarvamaa (Paide), Jogevamaa (Jogeva), Laanemaa (Haapsalu), Laane-Virumaa (Rakvere), Parnumaa (Parnu), Polvamaa (Polva), Raplamaa (Rapla), Saaremaa (Kuressaare), Tartumaa (Tartu), Valgamaa (Valga), Viljandimaa (Viljandi), Vorumaa (Voru)note: counties have the administrative center name following in parenthesesIndependence:20 August 1991 (declared); 6 September 1991 (recognized by the Soviet Union)National holiday:Independence Day, 24 February (1918); note - 24 February 1918 was the date Estonia declared its independence from Soviet Russia and established its statehood; 20 August 1991 was the date it declared its independence from the Soviet UnionConstitution:adopted 28 June 1992Legal system:civil law systemInternational law organization participation:accepts compulsory ICJ jurisdiction with reservations; accepts ICCt jurisdictionSuffrage:18 years of age; universal for all Estonian citizensExecutive branch:chief of state: President Toomas Hendrik ILVES (since 9 October 2006)head of government: Prime Minister Andrus ANSIP (since 12 April 2005)cabinet: Ministers appointed by the prime minister, approved by Parliament(For more information visit the World Leaders website )elections: president elected by Parliament for a five-year term (eligible for a second term); if a candidate does not secure two-thirds of the votes after three rounds of balloting in the Parliament, then an electoral assembly (made up of Parliament plus members of local councils) elects the president, choosing between the two candidates with the largest number of votes; election last held on 29 August 2011 (next to be held in the fall of 2016); prime minister nominated by the president and approved by Parliamentelection results: Toomas Hendrik ILVES reelected president; parliamentary vote - Toomas Hendrik ILVES 73, Indrek TARAND 25Legislative branch:unicameral Parliament or Riigikogu (101 seats; members elected by popular vote to serve four-year terms)elections: last held on 6 March 2011 (next to be held in March 2015)election results: percent of vote by party - Estonian Reform Party 28.6%, Center Party of Estonia 23.3%, IRL 20.5%, SDE 17.1%, Estonian Greens 3.8%, Estonian People's Union 2.1%, other 4.6%; seats by party - Estonian Reform Party 33, Center Party 21, IRL 23, SDE 19, unaffiliated 5Judicial branch:highest court(s): Supreme Court (consists of the chief justice and organized into the Civil Chamber with a chamber chairman and 6 justices, the Criminal Chamber with a chamber chairman and 5 justices, the Administrative Law Chamber with a chamber chairman and 4 justices, and the Constitutional Review Chamber with 9 members - the chief justice and 2 justices from the Civil Chamber, 3 from the Criminal Chamber and 3 from the Administrative chamber)judge selection and term of office: the chief justice is proposed by the president and appointed by the Riigikogu; other justices proposed by the chief justice and appointed by the Riigikogu; justices appointed for lifesubordinate courts: circuit (appellate) courts; administrative, county, city, and specialized courtsPolitical parties and leaders:Center Party of Estonia (Keskerakond) [Edgar SAVISAAR]Estonian Greens (Rohelised) [Aleksander LAANE]Estonian Conservative People's Party (Konservatiivne Rahvaerakond) or EKRE [Margo MILJAND]Estonian Reform Party (Reformierakond) [Andrus ANSIP]Social Democratic Party or SDE [Sven MIKSER]Union of Pro Patria and Res Publica (Isamaa je Res Publica Liit) or IRL [Urmas REINSALU]International organization participation:Australia Group, BA, BIS, CBSS, CD, CE, EAPC, EBRD, ECB, EIB, EMU, ESA (cooperating state), EU, FAO, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC (national committees), ICRM, IDA, IFC, IFRCS, IHO, ILO, IMF, IMO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, ITUC (NGOs), MIGA, NATO, NIB, NSG, OAS (observer), OECD, OIF (observer), OPCW, OSCE, PCA, Schengen Convention, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNHCR, UNTSO, UPU, WCO, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTODiplomatic representation in the US:chief of mission: Ambassador Marina KALJURANDchancery: 2131 Massachusetts Avenue NW, Washington, DC 20008telephone: [1] (202) 588-0101FAX: [1] (202) 588-0108consulate(s) general: New YorkDiplomatic representation from the US:chief of mission: Ambassador Jeffrey LEVINEembassy: Kentmanni 20, 15099 Tallinnmailing address: use embassy street addresstelephone: [372] 668-8100FAX: [372] 668-8134Flag description:three equal horizontal bands of blue (top), black, and white; various interpretations are linked to the flag colors; blue represents faith, loyalty, and devotion, while also reminiscent of the sky, sea, and lakes of the country; black symbolizes the soil of the country and the dark past and suffering endured by the Estonian people; white refers to the striving towards enlightenment and virtue, and is the color of birch bark and snow, as well as summer nights illuminated by the midnight sunNational symbol(s):barn swallow, cornflowerNational anthem:name: ""Mu isamaa, mu onn ja room"" (My Native Land, My Pride and Joy)lyrics/music: Johann Voldemar JANNSEN/Fredrik PACIUSnote: adopted 1920, though banned between 1940 and 1990 under Soviet occupation; the anthem, used in Estonia since 1869, shares the same melody with that of Finland but has different lyricsEconomy ::EstoniaEconomy - overview:Estonia, a member of the European Union and the eurozone since 2004, has a modern market-based economy and one of the higher per capita income levels in Central Europe and the Baltic region. Estonia's successive governments have pursued a free market, pro-business economic agenda and have wavered little in their commitment to pro-market reforms. The current government has followed sound fiscal policies that have resulted in balanced budgets and low public debt. The economy benefits from strong electronics and telecommunications sectors and strong trade ties with Finland, Sweden, Russia, and Germany. Tallinn's priority has been to sustain high growth rates - on average 8% per year from 2003 to 2007. Estonia's economy fell into recession in mid-2008 with GDP contracting 14.3% in 2009, as a result of an investment and consumption slump following the bursting of the real estate market bubble and a decrease in export demand as result of economic slowdown in the rest of Europe. Estonia rebounded nearly 8% in 2011 and the Estonian economy now has one of the higher GDP growth rates in Europe. Estonia adopted the euro on 1 January 2011.GDP (purchasing power parity):$29.57 billion (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 113$28.64 billion (2011 est.)$26.45 billion (2010 est.)note: data are in 2012 US dollarsGDP (official exchange rate):$21.86 billion (2012 est.)GDP - real growth rate:3.2% (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 1038.3% (2011 est.)3.3% (2010 est.)GDP - per capita (PPP):$22,100 (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 66$21,400 (2011 est.)$19,700 (2010 est.)note: data are in 2012 US dollarsGross national saving:24.1% of GDP (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 5026.9% of GDP (2011 est.)23.1% of GDP (2010 est.)GDP - composition, by end use:household consumption: 50.1%government consumption: 18.8%investment in fixed capital: 24.5%investment in inventories: 5.8%exports of goods and services: 89.1%imports of goods and services: -88.3%(2012 est.)GDP - composition, by sector of origin:agriculture: 3.9%industry: 29.7%services: 66.4% (2012 est.)Agriculture - products:grain, potatoes, vegetables; livestock and dairy products; fishIndustries:engineering, electronics, wood and wood products, textiles; information technology, telecommunicationsIndustrial production growth rate:2.2% (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 95Labor force:695,000 (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 152Labor force - by occupation:agriculture: 4.2%industry: 20.2%services: 75.6% (2010)Unemployment rate:10.2% (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 10912.5% (2011 est.)Population below poverty line:17.5% (2010)Household income or consumption by percentage share:lowest 10%: 2.7%highest 10%: 27.7% (2004)Distribution of family income - Gini index:31.3 (2010)country comparison to the world: 10837 (1999)Budget:revenues: $8.144 billionexpenditures: $8.201 billion (2012 est.)Taxes and other revenues:37.2% of GDP (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 56Budget surplus (+) or deficit (-):-0.3% of GDP (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 53Public debt:5.7% of GDP (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 1505.9% of GDP (2011 est.)note: data cover general government debt, and includes debt instruments issued (or owned) by government entities, including sub-sectors of central government, state government, local government, and social security fundsFiscal year:calendar yearInflation rate (consumer prices):3.9% (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 1215% (2011 est.)Commercial bank prime lending rate:8% (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 1396.12% (31 December 2011 est.)Stock of narrow money:$8.104 billion (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 82$6.744 billion (31 December 2011 est.)note: this figure represents the US dollar value of Estonian kroon in circulation prior to Estonia's joining the Economic and Monetary Union (EMU); see entry for the European Union for money supply in the euro area; the European Central Bank (ECB) controls monetary policy for the 17 members of the EMU; individual members of the EMU do not control the quantity of money circulating within their own bordersStock of broad money:$12.11 billion (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 99$11.73 billion (31 December 2011 est.)Stock of domestic credit:$19.04 billion (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 85$19.14 billion (31 December 2011 est.)Market value of publicly traded shares:$1.611 billion (31 December 2011)country comparison to the world: 97$2.26 billion (31 December 2010)$2.654 billion (31 December 2009)Current account balance:$498 million (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 47$477 million (2011 est.)Exports:$16.16 billion (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 78$16.78 billion (2011 est.)Exports - commodities:machinery and electrical equipment 21%, wood and wood products 9%, metals 9%, furniture 7%, vehicles and parts 5%, food products and beverages 4%, textiles 4%, plastics 3%Exports - partners:Sweden 16.8%, Finland 15.3%, Russia 12.7%, Latvia 9.2%, Lithuania 5.7%, Germany 4.8% (2012)Imports:$17.05 billion (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 83$17.09 billion (2011 est.)Imports - commodities:machinery and electrical equipment, mineral fuels, chemical products, foodstuffs, plastics, textilesImports - partners:Finland 15.1%, Germany 10.7%, Sweden 10.7%, Latvia 10%, Lithuania 9%, Poland 6.6%, China 4.4%, Russia 4.1% (2012)Reserves of foreign exchange and gold:$246.4 million (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 156$207.5 million (31 December 2011 est.)Debt - external:$25.55 billion (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 77$25.01 billion (31 December 2011 est.)Stock of direct foreign investment - at home:$17.45 billion (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 70$16.65 billion (31 December 2011 est.)Stock of direct foreign investment - abroad:$6.609 billion (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 61$7.359 billion (31 December 2011 est.)Exchange rates:kroon (EEK) per US dollar -0.778 (2012 est.)0.72 (2011 est.)11.81 (2010 est.)11.23 (2009)10.7 (2008)Energy ::EstoniaElectricity - production:12.89 billion kWh (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 88Electricity - consumption:7.755 billion kWh (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 95Electricity - exports:4.354 billion kWh (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 30Electricity - imports:1.1 billion kWh (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 62Electricity - installed generating capacity:2.661 million kW (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 91Electricity - from fossil fuels:94.6% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 69Electricity - from nuclear fuels:0% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 83Electricity - from hydroelectric plants:0.3% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 145Electricity - from other renewable sources:5.1% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 36Crude oil - production:7,700 bbl/day (2011 est.)country comparison to the world: 83Crude oil - exports:0 bbl/day (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 105Crude oil - imports:0 bbl/day (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 179Crude oil - proved reserves:0 bbl (1 January 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 127Refined petroleum products - production:0 bbl/day (2008 est.)country comparison to the world: 173Refined petroleum products - consumption:26,340 bbl/day (2011 est.)country comparison to the world: 121Refined petroleum products - exports:0 bbl/day (2008 est.)country comparison to the world: 173Refined petroleum products - imports:23,270 bbl/day (2008 est.)country comparison to the world: 100Natural gas - production:0 cu m (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 123Natural gas - consumption:701 million cu m (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 96Natural gas - exports:0 cu m (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 92Natural gas - imports:701 million cu m (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 64Natural gas - proved reserves:0 cu m (1 January 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 131Carbon dioxide emissions from consumption of energy:20.56 million Mt (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 81Communications ::EstoniaTelephones - main lines in use:471,900 (2011)country comparison to the world: 101Telephones - mobile cellular:1.863 million (2011)country comparison to the world: 142Telephone system:general assessment: foreign investment in the form of joint business ventures greatly improved telephone service with a wide range of high quality voice, data, and Internet services availabledomestic: substantial fiber-optic cable systems carry telephone, TV, and radio traffic in the digital mode; Internet services are widely available; schools and libraries are connected to the Internet, a large percentage of the population files income-tax returns online, and online voting was used for the first time in the 2005 local electionsinternational: country code - 372; fiber-optic cables to Finland, Sweden, Latvia, and Russia provide worldwide packet-switched service; 2 international switches are located in Tallinn (2011)Broadcast media:the publicly owned broadcaster, Eesti Rahvusringhaaling (ERR), operates 2 TV channels and 5 radio networks; growing number of private commercial radio stations broadcasting nationally, regionally, and locally; fully transitioned to digital television in 2010; national private TV channels expanding service; a range of channels are aimed at Russian-speaking viewers; high penetration rate for cable TV services with more than half of Estonian households connected (2008)Internet country code:.eeInternet hosts:865,494 (2012)country comparison to the world: 49Internet users:971,700 (2009)country comparison to the world: 102Transportation ::EstoniaAirports:18 (2013)country comparison to the world: 141Airports - with paved runways:total: 13over 3,047 m: 22,438 to 3,047 m: 81,524 to 2,437 m: 2914 to 1,523 m: 1 (2013)Airports - with unpaved runways:total: 51,524 to 2,437 m: 1914 to 1,523 m: 1under 914 m:3 (2013)Heliports:1 (2012)Pipelines:gas 868 km (2013)Railways:total: 1,196 kmcountry comparison to the world: 85broad gauge: 1,196 km 1.520-m and 1.524-m gauge (133 km electrified) (2011)Roadways:total: 58,412 km (includes urban roads)country comparison to the world: 75paved: 10,427 km (includes 115 km of expressways)unpaved: 47,985 km (2011)Waterways:335 km (320 km are navigable year round) (2011)country comparison to the world: 91Merchant marine:total: 25country comparison to the world: 89by type: cargo 4, chemical tanker 1, passenger/cargo 18, petroleum tanker 2foreign-owned: 3 (Germany 1, Norway 2)registered in other countries: 63 (Antigua and Barbuda 10, Belize 1, Cambodia 1, Canada 1, Cook Islands 1, Cyprus 6, Dominica 6, Finland 2, Latvia 3, Malta 16, Russia 1, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines 8, Sierra Leone 2, Sweden 3, Venezuela 1, unknown 1) (2010)Ports and terminals:major seaport(s): Kuivastu, Kunda, Muuga, Parnu Reid, Sillamae, TallinnMilitary ::EstoniaMilitary branches:Estonian Defense Forces (Eesti Kaitsevagi): Land Force (Maavagi), Navy (Merevagi), Air Force (Ohuvagi), Defense League (Kaitseliit) (2012)Military service age and obligation:18-27 for compulsory military or governmental service, conscript service requirement 8-11 months depending on education; NCOs, reserve officers, and specialists serve 11 months (2013)Manpower available for military service:males age 16-49: 291,801females age 16-49: 302,696 (2010 est.)Manpower fit for military service:males age 16-49: 210,854females age 16-49: 251,185 (2010 est.)Manpower reaching militarily significant age annually:male: 6,668female: 6,309 (2010 est.)Military expenditures:2% of GDP (2005 est.)country comparison to the world: 67Transnational Issues ::EstoniaDisputes - international:Russia and Estonia in May 2005 signed a technical border agreement, but Russia in June 2005 recalled its signature after the Estonian parliament added to its domestic ratification act a historical preamble referencing the Soviet occupation and Estonia's pre-war borders under the 1920 Treaty of Tartu; Russia contends that the preamble allows Estonia to make territorial claims on Russia in the future, while Estonian officials deny that the preamble has any legal impact on the treaty text; Russia demands better treatment of the Russian-speaking population in Estonia; as a member state that forms part of the EU's external border, Estonia implements strict Schengen border rules with RussiaRefugees and internally displaced persons:stateless persons: 94,235 (2012); note - after becoming independent in 1991, automatic citizenship was restricted to those who were Estonian citizens prior to the 1990 Soviet occupation and their descendants; thousands of ethnic Russians remained stateless when forced to choose between passing Estonian language and citizenship tests or applying for Russian citizenship; one reason for demurring on Estonian citizenship was to retain the right of visa-free travel to Russia; stateless residents can vote in local elections but not general elections; stateless parents who have been lawful residents of Estonia for at least five years can apply for citizenship for their children before they turn 15Illicit drugs:growing producer of synthetic drugs; increasingly important transshipment zone for cannabis, cocaine, opiates, and synthetic drugs since joining the European Union and the Schengen Accord; potential money laundering related to organized crime and drug trafficking is a concern, as is possible use of the gambling sector to launder funds; major use of opiates and ecstasy"
The World Factbook. 2014.
